XPS and XAES characterisation
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and x-ray-induced Auger electron spectroscopy analyses were performed to characterize NiP coating on the iron substrate. This electroless coating is commonly used for its outstanding corrosion resistance, but it is currently of interest as a hydrogen permeation barrier (HPB) for green hydrogen storage and transportation; thus, NiP coatings are relevant for energy and for the environment.
Electroless NiP coatings were deposited from a commercial nickel hypophosphite bath at pH 4.8 and 88 °C. X-ray diffraction provided evidence that the sample is amorphous; atomic force microscopy (AFM) showed the presence of nanocrystallites.
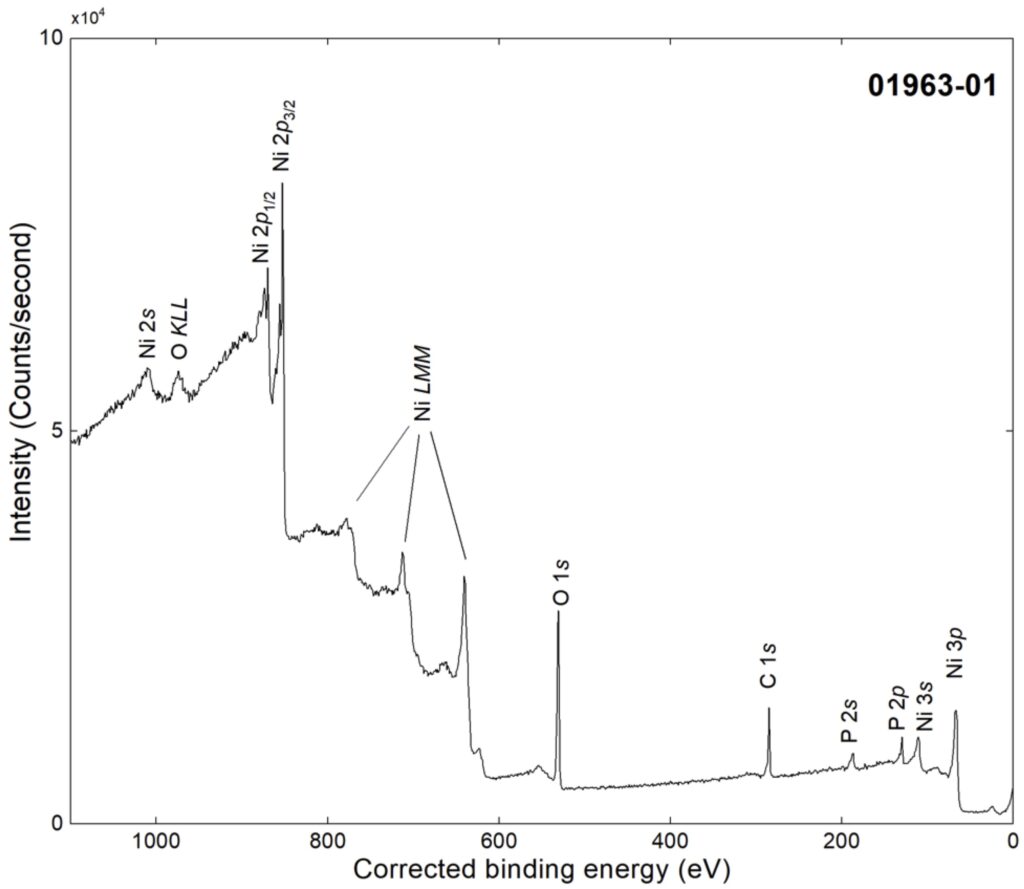
This work uses X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray-induced Auger electron spectroscopy (XAES) to characterize the NiP surface
The NiP alloy, following mechanical polishing, showed a nickel spectral region which includes the contribution of the NiP coating and that of the surface film made of nickel phosphate. The signals at 852.6 eV and 869.8 eV are due to the spin–orbit coupling components, Ni 2p3/2 and Ni 2p1/2, respectively of the NiP and are together with the satellites.
Publication: D. Biggio, B. Elsener, M. Fantauzzi, A. Rossi, XPS study of electroless NiP coating on iron substrate, Surface Science Spectra 31 (2024) 024003 doi: 10.1116/6.0003733