Organic Memories
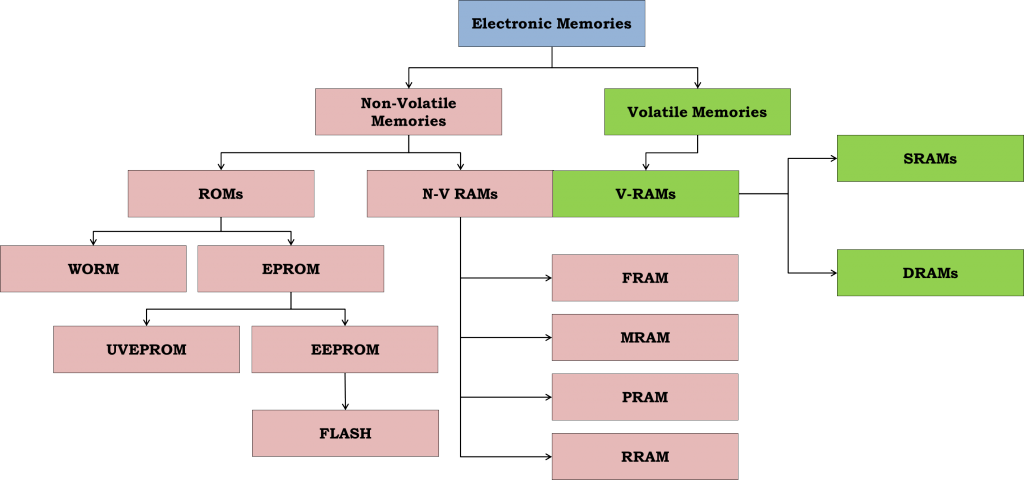
An electronic memory is a component, device or recording medium used to store data for retrieval on a temporary or permanent basis for use in a computer or other digital electronic devices. It is one of the fundamental components of all modern computers and electronic systems.
Electronic memories can be divided into two primary categories:
- volatile memory, which requires a costant power supply to retain the stored information: it loses written data as soon as the system is turned off;
- non-volatile memory, which can retain the stored information even when the electrical power supply has been turned off.
Currently, DRAMs and FLASH memories constitute the biggest part of the semiconductor memory market. In spite of the wide application in commercial products, these conventional memory technologies have some important disadvantages. The hard disk is the cheapest technology, but it is volatile and its access and program times are limited to several ms. FLASH memories offer a considerable decrease in access times, but program times remain long and cost/bit is much higher. All these limitations of conventional memories have led to a considerable amount of research activity for new non-volatile memory technologies.
The focus of research is on obtaining non-volatile, fast, high-density, low-power consumption, high data transfer rate and reliable memories. Numerous types of memories have been proposed in order to overcome the shortcomings of conventional memories. Among the emerging candidates for non-volatile memories, organic materials are promising candidates for future molecular-scale device applications. Organic electronics provide mechanical flexibility and stretchability as well as low-cost manufacturability, complementing the computing power of silicon electronics. Moreover, the low-temperature fabrication process of organic memory also offers benefits for integrating memory devices into stretchable electronic systems on an elastic polymeric substrate.
In an attempt to create a novel organic memory, several types of memory devices based on organic and polymeric materials have been evaluated. It is possible to characterize the organic memory devices that have so far appeared in the literature into one of two broad categories:
- transistor-based memories
- resistor-based memories.